Recent News
-

Model developed by Hopkins engineers could guide treatment plans
-

MechE professor and interim co-director of the JHU Data Science and AI Institute spoke with 555 Penn about how he's using AI tools and why we need AI regulation
-

Novel UAV platform combines custom hardware and neural networks for better pick-and-place operations
-

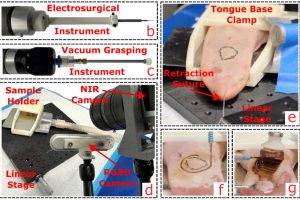
“We’ve sent the robot to make an incision before, but this is the first time we’ve done a bulk resection and taken a tumor out fully."
-

Results have implications for understanding biological systems.
-

In new study, researchers find that prosthesis with both haptic feedback and autonomous control allowed users to complete the tasks with greater performance and lower mental effort.
-

Researchers to try to figure out how Drosophila, the humble fruit fly, controls its movements so precisely and elegantly to inform the design of better robotic systems.
-

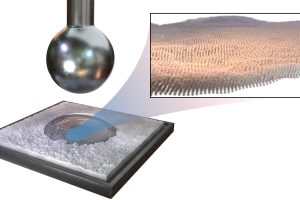
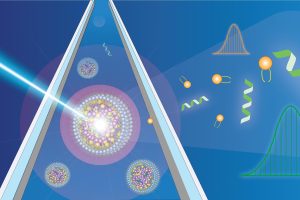
Breakthrough medical technology like mRNA vaccines rely on tiny nanoparticles to deliver medicine to cells. A new device will help drug manufacturers and evaluators like the FDA more precisely measure genetic payloads to evaluate drug effectiveness.